티스토리 뷰
DFS (Depth First Search) (깊이 우선 탐색)
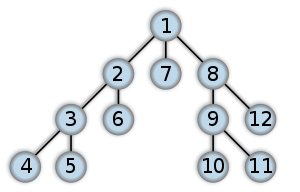
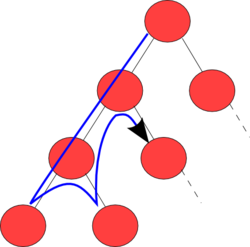
- LIFO(Last-In First-Out), Stack 활용
PseudoCode

recursive

non-recursive 1

non-recursive 2
예제
|
Input |
Output |
|
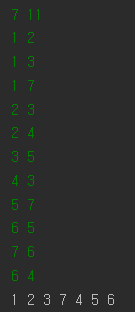
첫 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 M이 주어집니다. 다음 M줄에 간선의 관계 시작정점 u와 도착정점 v가 주어집니다. |
입력에 따른 깊이 우선 탐색 결과를 출력합니다. |

import java.util.*;
public class Test {
static boolean edge[][];
static boolean visited[];
static int n;
static int m;
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
m = scanner.nextInt();
edge = new boolean[n + 1][n + 1];
visited = new boolean[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u = scanner.nextInt();
int v = scanner.nextInt();
edge[u][v] = true;
}
dfs(1);
}
public static void dfs(int cur) {
visited[cur] = true;
System.out.print(String.valueOf(cur) + ' ');
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (visited[i] || !edge[cur][i]) continue; // already visited or not connected.
dfs(i);
}
}
}
BFS (Breadth First Search) (너비 우선 탐색)

- FIFO (First-In First-Out), Queue 활용
PseudoCode
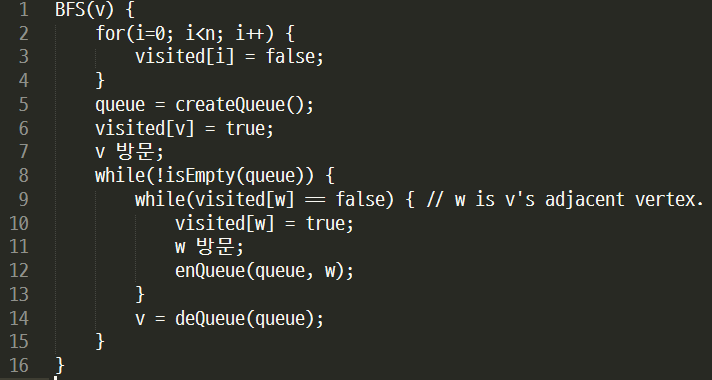
non-recursive
예제
|
Input |
Output |
|
첫 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 M이 주어집니다. 다음 M줄에 간선의 관계 시작정점 u와 도착정점 v가 주어집니다. |
입력에 따른 너비 우선 탐색 결과를 출력합니다. |
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
static boolean edge[][];
static boolean visited[];
static int n;
static int m;
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
m = scanner.nextInt();
edge = new boolean[n + 1][n + 1];
visited = new boolean[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u = scanner.nextInt();
int v = scanner.nextInt();
edge[u][v] = true;
}
bfs(1);
}
public static void bfs(int cur) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
visited[cur] = true;
q.add(cur);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int here = q.remove();
System.out.print(String.valueOf(here) + ' ');
for (int there = 1; there <= n; there++) {
if (visited[there] || (!edge[here][there])) continue;
visited[there] = true;
q.add(there);
}
}
}
}
DFS vs BFS
DFS
- 장점
- 현 경로상의 노드들만 기억하면 되서, 저장공간 수요가 적다.
- 목표노드가 깊은단계에 있을경우 빠르게 구할수있다.
- 단점
- 해가 없는 경로에 깊이 빠질 가능성이 있다. 따라서 미리 지정한 깊이제한(depth bound)까지만 탐색하면 유용할것. with Backtracking
- 얻은 해가 최단경로라는 보장이 없다. 목표에 이르는 경로가 다수인 경우, DFS는 해에 도달하면 탐색을 끝내버리므로 최적이 아닐수있음.
BFS
- 장점
- 최단 길이 경로를 보장한다.
- 단점
- 경로가 길 경우, branch가 증가하여 저장공간을 많이 필요로 한다.
- 해가 존재하지않으면, 모든 그래프를 탐색후 실패로 끝난다. 무한그래프라면 해를 찾지도 끝내지도 못한다.
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 알고리즘) Graph - Dijkstra/Floyd-Warshall/Bellman-Ford 's Alg (distance) (0) | 2019.09.13 |
|---|---|
| 알고리즘) Graph - MST (Minimum_Cost Spanning Tree) using Prim/Kruskal's Algorithm (0) | 2019.09.13 |
| 알고리즘) Two Pointer, Sliding Window (0) | 2019.09.12 |
| 알고리즘) Heap/Tree Sort (힙/트리 정렬) (0) | 2019.09.12 |
| 알고리즘) Shell/Radix Sort (셸/기수 정렬) (0) | 2019.09.12 |
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
TAG
- 프로그래머스
- Data Structure
- OneToMany
- dfs
- mysql
- Java
- FRAGMENT
- 리버싱
- Android
- Android Studio
- 개발자
- Vo
- sort
- reversing
- git
- 해외여행
- 우아한 테크코스
- graph
- 웹해킹
- socket
- queue
- webhacking.kr
- bfs
- 회고
- Stack
- javascript
- brute-force
- JPA
- Algorithm
- C
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
글 보관함
